June 24, 2021
【研究紹介】自動運転の自己位置推定とデジタル地図に関する研究(上條俊介准教授)Research on Self-Localization and Digital Map for Autonomous Vehicles (Associate Professor KAMIJO Shunsuke)
上條研究室では、自動運転に関連して深層学習を活用した物体検出、シーン理解、自己位置推定およびデジタル地図等、必要不可欠なテーマを網羅的に研究しています。今回は、その中でも自己位置推定とデジタル地図の研究についてご紹介します。
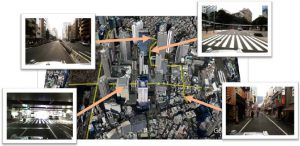
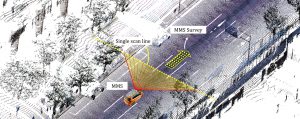
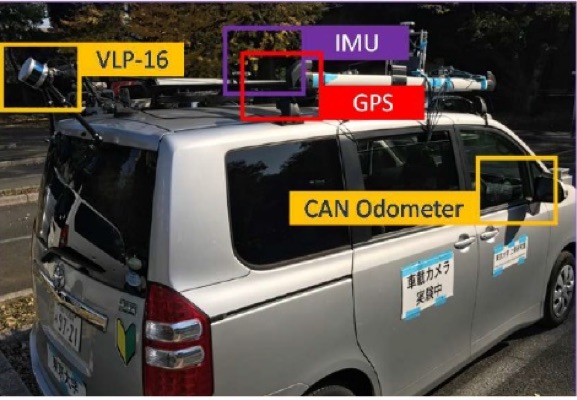
現在の自動運転の研究で多く使用されているのは、点群(point cloud)という形式のデータです。各点はLiDARやステレオカメラでサンプリングされた三次元座標情報をもっています。ビル、道路、信号機などの構造物がこのような点群データで構成されます。自動運転では、デジタル地図をレファレンスとして、走行中に取得された点群データのマッチングを行うことで自己の位置推定を行います。
一般にSLAM(Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)で作成された点群データは、局所的な相対位置関係は正確ですが、大域的な位置関係には誤差が生じます。例えば、1kmを走行すれば絶対精度として5m程度の歪みを生じえます。この問題は、航空写真のように絶対座標精度が高い情報とpoint cloudのマッチングを行うことで解決できます[1]。また、自動運転以外の目的のデジタル地図はベクトルデータで構成されている場合が多く、その中で点群地図はむしろ特異な存在といえます[2]。そこで、このようなデモ用の点群地図と現実のデジタル地図とのギャップを埋める研究を行っています[1][2]。
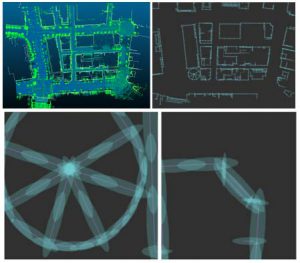
また、LiDARで計測可能な範囲内に構造物が少ない場合や単調な構造物が続く場所では、そもそも位置推定の精度が低下し、1m以上の誤差になることも稀ではありません[3]。このような静的要因に加えて、バスやトラックなどの背が高い周辺車両によってLiDARビームが遮蔽されるというような動的要因によっても位置推定精度が著しく低下します[4]。そこで、位置推定精度の環境依存性を、位置決定に必要な情報量という視点で定量化することを試みています[3][4]。
[1] Mahdi Javanmardi, Ehsan Javanmardi, Yanlei Gu, Shunsuke Kamijo, “Automatic Calibration of 3D Mobile Laser Scanning using Aerial Surveillance Data for Precise Urban Mapping”, IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2017), Redondo Beach, California USA, June, 2017.
[2] Ehsan Javanmardi, Mahdi Javanmardi, Yanlei Gu, Shunsuke Kamijo, “Autonomous Vehicle Self-Localization Based on Multilayer 2D Vector Map and Multi-channel LiDAR”, IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2017), Redondo Beach, California USA, June, 2017.
[3] Ehsan Javanmardi, Mahdi Javanmardi, Yanlei Gu, Shunsuke Kamijo, “Adaptive Resolution Refinement of NDT Map Based on Localization Error Modeled by Map Factors”, 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC2018), Maui, HI, USA, Nov. 2018.
[4] Yuki Endo, Ehsan Javanmardi, Yanlei Gu, Shunsuke Kamijo, “Evaluation of High Definition Map-Based Self-Localization Against Occlusions in Urban Area”, to appear in IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2021), Nagoya, July 2021.
記事:上條俊介(准教授)
Kamijo Lab. covers a wide range of topics related to autonomous vehicles, such as object detection and scene understanding by deep learning techniques, and self-localization and digital mapping. In this article, we would like to introduce research on self-localization and digital mapping.
Currently, point cloud data is generally used for research and demonstration of Autonomous Driving. Each point consists of three-dimensional coordinates detected by LiDAR or stereo vision sensors. Buildings and roadside facilities such as traffic signals are configured with point cloud data in the digital map. Autonomous vehicles estimate their position by matching detected points to the point clouds in the digital map as the reference.
Generally, SLAM can provide point clouds with high accuracy of local alignment that is relatively accurate in the digital map. On the other hand, SLAM suffers from lower accuracy of global alignment that is absolutely accurate in the digital map. For example, a digital map might have around five meters of error in global alignment when SLAM is applied to 1km of driving data. This problem can be solved by matching point cloud data to an airborne image which has accurate absolute coordinates [1]. Popular digital maps with purposes other than autonomous driving consist of vector data. Thus, the point cloud map is considered unique for the demonstration of autonomous driving [2], and we aim to solve the problems of those gaps between the point cloud map and existing popular digital maps [1][2].
The error of self-localization increases inherently when the environment has fewer or featureless buildings and structures [3]. An error of more than 1m is not unusual in such circumstances. In addition to such static factors, dynamic factors such as occlusion of the LiDAR beam by tall buses and trucks strongly affect the accuracy of self-localization [4]. We aim to formulate a quantitative method to evaluate the localization error affected by both the static and dynamic environments [3][4].
[1] Mahdi Javanmardi, Ehsan Javanmardi, Yanlei Gu, Shunsuke Kamijo, “Automatic Calibration of 3D Mobile Laser Scanning using Aerial Surveillance Data for Precise Urban Mapping”, IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2017), Redondo Beach, California USA, June, 2017.
[2] Ehsan Javanmardi, Mahdi Javanmardi, Yanlei Gu, Shunsuke Kamijo, “Autonomous Vehicle Self-Localization Based on Multilayer 2D Vector Map and Multi-channel LiDAR”, IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2017), Redondo Beach, California USA, June, 2017.
[3] Ehsan Javanmardi, Mahdi Javanmardi, Yanlei Gu, Shunsuke Kamijo, “Adaptive Resolution Refinement of NDT Map Based on Localization Error Modeled by Map Factors”, 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC2018), Maui, HI, USA, Nov. 2018.
[4] Yuki Endo, Ehsan Javanmardi, Yanlei Gu, Shunsuke Kamijo, “Evaluation of High Definition Map-Based Self-Localization Against Occlusions in Urban Area”, to appear in IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV2021), Nagoya, July 2021.
Text: Shunsuke Kamijo (Associate professor)
English proofreading: David Buist (Senior project specialist)
主担当教員Associated Faculty Members
准教授
上條 俊介
- 先端表現情報学コース
- 情報学環教育部
Associate Professor
KAMIJO, Shunsuke
- Emerging design and informatics course
- Undergraduate research student program